
How does artificial intelligence benefit e-commerce?
Surely you’ve heard of artificial intelligence (AI)?
Although for some people it still only evokes science fiction and robotics, it is nevertheless part of all aspects of our daily lives. From automated cash registers to advanced security checks at airports: artificial intelligence is now just about everywhere. And, little by little, it is beginning to penetrate e-commerce.
In fact, many companies are already leveraging the latest advances in AI and machine learning(ML) to provide a better shopping experience for their customers. As it improves, artificial intelligence could and most likely will permanently change the e-commerce landscape in the years to come.
AI and ML in e-commerce
By definition, artificial intelligence is the ability of a machine to perform tasks in an “intelligent” way, such as learning and decision-making, as a human being would.
Machine learning is a current application of AI based on the idea that we should be able to give machines access to data and let them learn on their own.
Applied to e-commerce and marketing, machine learning refers to the various methods of data analysis in which computers find information without being told exactly where to look for it. ML algorithms, when exposed to massive amounts of data, can extract patterns and use them to generate insights or predictions about future conditions.
Although still relatively new, artificial intelligence has already had a huge impact in a short period of time on industries such as finance and healthcare. And the benefits of AI are now starting to spread to e-commerce.
It is important to note that artificial intelligence by itself is not a product, but a powerful tool to create better products that meet customer needs. Yes, even if it may seem paradoxical for a machine, the greatest strength of artificial intelligence is that it can help e-commerce to create a more human customer experience by personalizing it!
Indeed, an online sales business generates monumental volumes of data from dozens of channels. There is even too much data for a human being to know where to look or even what to look for – the perfect conditions for machine learning.
Thus, many e-tailers are already trying to differentiate themselves by using forms of AI to better understand their customers, generate new leads and provide an improved customer experience.
Examples of uses of AI in e-commerce
Creation of personalized recommendations
Personalization in e-commerce is not new. Many companies and e-tailers currently use a filtering system to provide customers with product recommendations. These filters typically base their results on bestseller data, viewing history and other general aggregation parameters.
At best, the most successful recommendation systems can remember what your customer likes.
But, as you will agree, it is all a bit impersonal. “People who bought this product also bought this product” is not the best way to personalize an offer.
That’s where AI comes in.
While the word “artificial” connotes a certain dehumanization, artificial intelligence instead allows merchants to build a more personalized customer experience by providing recommendations to subscribers based on their preferences.
In what way? Thanks to the ability of AI to analyze large data sets more efficiently than a human being. This means that the technology can quickly analyze different aspects of browsing behavior. Every time a user reviews a product, posts or even tweets about it, the information can be used.
Artificial intelligence technology is also able to learn the interests, passions and triggers that make a consumer more likely to make a purchase.
This means that millions of transactions and communications can be analyzed each day to target offers to a single customer.
By exposing machine learning algorithms to truly massive amounts of data, merchants can thus build automated analytical models that are not limited by the ability of humans to suggest why certain people buy particular products.
Such AI-driven applications are discovering better ways to model user behavior. Finally, technology facilitates :
- the sales process, by identifying who is most likely to buy a product (based on past purchase history, demographics, etc.)
- Personalization of the sales cycle, by engaging the right prospects with the right message at the right time
An example of using AI for personalized recommendations: Starbucks recently launched “My Starbucks Barista,” which uses AI to allow customers to place orders by voice or via messaging. The algorithm relies on a variety of inputs, including account information, customer preferences, purchase history, third-party data and contextual information. This allows the coffee giant to provide more personalized messages and recommendations to its customers.
Find potential customers
According to a recent study, at least one third of prospects are not followed up by the sales team. This means that pre-qualified potential buyers interested in your product or service end up in the trash.
In addition, many companies are overloaded with customer data that they do little or nothing with. However, it is a gold mine that can be used to improve the sales cycle.
In retail, artificial intelligence is used, for example, with facial recognition to capture a customer’s behavior in a store. Basically, if a consumer lingers in front of a product – a coffee maker, for example – this information will be stored for use the next time they visit.
As the AI improves and develops, you may even start seeing special offers on your computer screen based on how long you wait in the store or even how you react to a product! For example, Microsoft offers “Mall kiosk”, which recommends products based on facial or voice recognition of reactions.
Creating an efficient sales process with a virtual assistant
Now, with virtual assistants, online businesses can leverage AI to select and recommend useful and desired products to a shopper in a meaningful way, saving the shopper from having to do all the work of searching through the catalog.
For example, integrating artificial intelligence with your CRM will allow you to personalize your solutions and create an effective sales message. In fact, if your AI system enables natural language learning and voice input, like Siri or Alexa, your CRM will respond to customer inquiries, solve their problems, and even identify new sales opportunities.
Better yet? Some AI-driven CRM systems can multitask to handle all these functions and more.
In this case, artificial intelligence helps users dive deeper into e-commerce product catalogs to find the perfect item that might otherwise go undiscovered.
There are also several online virtual assistant technologies. These bots use large data sets, collected in real time, to “learn” the shopping habits, interests and personal tastes of users.
Example of an online virtual assistant: you may have heard of “Mona”, the virtual business assistant developed by former Amazon employees. It helps simplify mobile shopping and provides customers with the best deals to suit their preferences. The more time the user spends interacting with the Mona robot, the better he will know it.
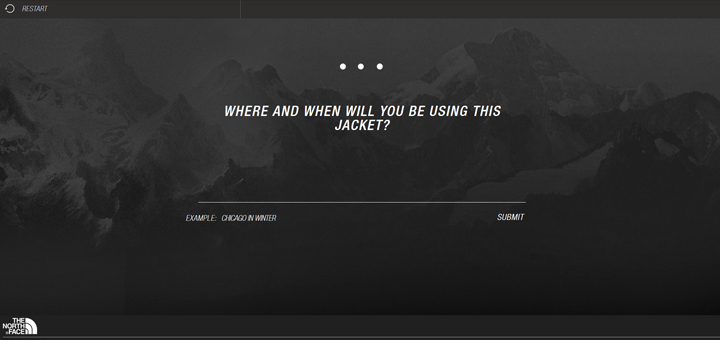
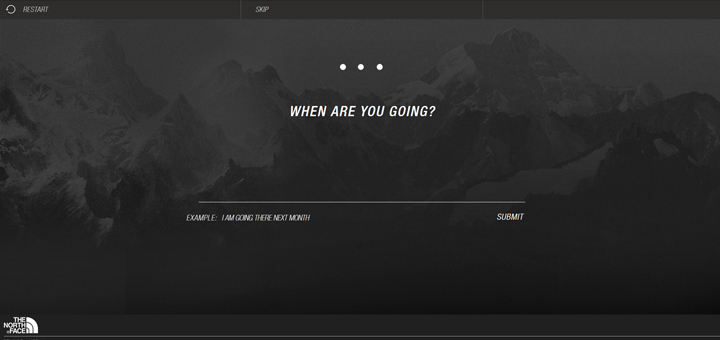
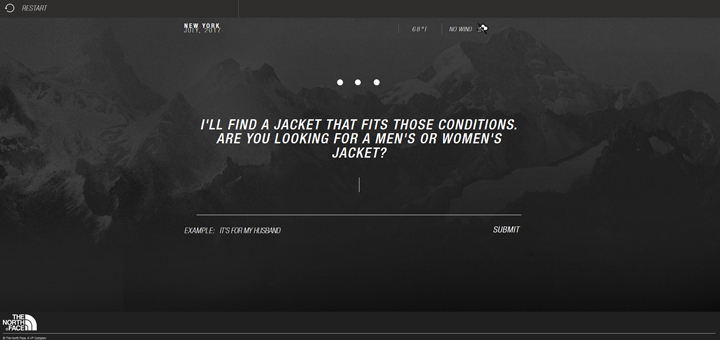
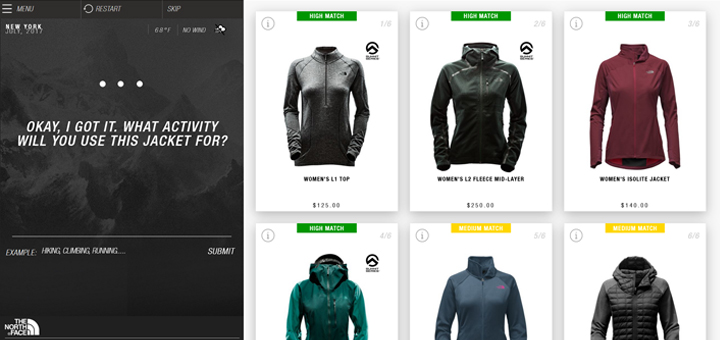
An example of the use of virtual assistants: The North Face brand is harnessing the power of virtual assistants to get to know its customers better while offering tailored recommendations. With the help of IBM’s intelligence solution called Watson, the company allows shoppers to discover their ideal jacket. To do this, customers are asked several questions, such as: “Where and when will you use your jacket? IBM’s software then analyzes hundreds of products to find the best matches based on responses correlated with other data, such as weather conditions. To get an idea, you can test the tool here.
Better search results
At least 30% of online shoppers use the search function of an e-commerce. However, this is often a tedious task for the consumer who is forced to choose and then refine a keyword that accurately describes the product they are looking for.
The scenario often goes like this: a consumer enters “smartphone with the best camera” in the search bar. While a human interlocutor would immediately understand the request, or ask questions to get more details about the customer’s needs, the digital results provided are often off the mark. In short, in the majority of cases, the search does not lead to the expected result.
This is due to the lack of context about the user, rigid and irrelevant filters, and problems with keyword understanding. In fact, the algorithms of these e-commerce search engines have neither the practical intelligence nor the ability to understand a query with the nuances of the language.
The key is to use the power of machine learning to improve results for consumers using search. ML can also generate a search ranking, which allows the site to sort search results by relevance, instead of by keyword.
By doing so, e-commerce platforms will be able to turn a massive number of failed search experiences into successful conversions.
To replace text searches, a solution is also starting to be implemented: visual search – a technology that uses artificial intelligence to analyze a photo submitted by a customer, then find the desired product or products that match that image.
Visual search allows customers to take a picture of a product they like and then upload it. The AI software is then able to evaluate that specific product, its brand, shape, style, fabric, color, etc., and then offer suggestions for similar products that may be of interest to the customer.
Finally, in addition to using images to search for products they want to buy, consumers will be able to use voice search – the ability to search for items using speech. Voice search uses AI to understand what is being said and to improve voice and phrase recognition.
Voice search has been popularized with voice assistants like Alexa and Siri, increasingly forcing e-tailers to re-optimize their web pages, and especially their FAQs, to cater to voice-based searches.
To learn more, you can also read our article: how to adapt your e-commerce site to voice search?
Example of using AI for search results: one company that uses machine learning to deliver better search results is eBay. With millions of items listed, the auction site harnesses the power of AI and data to predict and display the most relevant search results.
Example of the use of visual search: one of the innovative companies in terms of visual search is Neiman Marcus. With its application ” Snap. Find. Shop. “The fashion and beauty brand allows users to take photos of items in the real world and then find them in the catalog.
Improved customer service
If your business deals with customers on a daily basis and you will encounter recurring issues or questions, creating a chatbot is a good way to provide information to customers faster and more efficiently than a customer service representative.
In simple terms, chatbots are automated programs that can “converse” with people to answer questions and execute specific task requests. They’ve been around for quite some time now, but have made considerable progress in their ability to adapt to the customer through the process of machine learning.
In practical terms, chatbots can help you reduce customer service costs and better engage with consumers 24/7.
They also provide a good opportunity to personalize recommendations for consumers based on conversation history and can actively take on some of the important responsibilities of running an online business, such as automating ordering processes.
To learn more, check out our article:
10 examples of chatbots to use to boost your business
Currently, bots have pre-recorded responses and do not detect the use of sarcasm or humor. But, in the near future, a chatbot will be able to analyze new parameters and opt for a more friendly and accurate response.
Without a doubt, artificial intelligence has already started to have an impact on e-commerce, developing the sales process in an intelligent way so that customers are no longer offered solutions that are neither suitable nor appropriate. And, day by day, AI is becoming more and more sophisticated. Over the next few years, the application of machine learning and AI to e-commerce will become an increasingly important differentiator in terms of performance. E-retailers who do not act to reap the benefits then risk being blindsided by the early adopters who are reshaping the e-commerce market and buyer expectations.










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.